Python for Data Science (3150713)

Q1. Discuss why python is a first choice for data scientists? Discuss Data Science Pipeline.
Ans:- Python has a unique attribute and is easy to use when it comes to quantitative and analytical computing.
- Python is widely used in data science and is a favorite tool along with being a flexible and open-sourced language.
- Its massive libraries are used for data manipulation and are very easy to learn even for a beginner data analyst.
- Apart from being an independent platform it also easily integrates with any existing infrastructure which can be used to solve the most complex problems.
-
Python is preferred over other data science tools because of following
features,
- Powerful and Easy to use
- Open Source
- Choice of Libraries
- Flexibility
- Visualization and Graphics
- Well supported
- Data science is partly art and partly engineering.
- The Data science pipeline requires the data scientist to follow particular steps in the preparation, analysis, and presentation of the data.
-
General steps in the pipeline are:
-
Preparing the data:
- The data we gathered from various sources may not come directly in the structured format.
- We need to transform the data into a structured format.
- Transformation may require changing data types, the order in which data appears, and even the creation of missing data.
-
Performing data analysis:
- Data science provides access to a larger set of statistical methods and algorithms.
- Sometimes a single approach may not provide the desired output, we need to use multiple algorithms to get the result.
- The use of trial and error is part of the data science art.
-
Learning from data:
- As we iterate through various statistical analysis methods and apply algorithms to detect patterns, we begin learning from the data.
- After learning from the data, the result of the algorithm may be different than initially, we predict the output.
-
Visualizing:
- Visualization means seeing the patterns in the data and then being able to react to those patterns.
- It also means being able to see when data is not part of the pattern.
-
Obtaining insights and data products:
- The insights you obtain from manipulating and analyzing the data help you to perform real-world tasks. For example, you can use the results of an analysis to make a business decision.
-
Preparing the data:

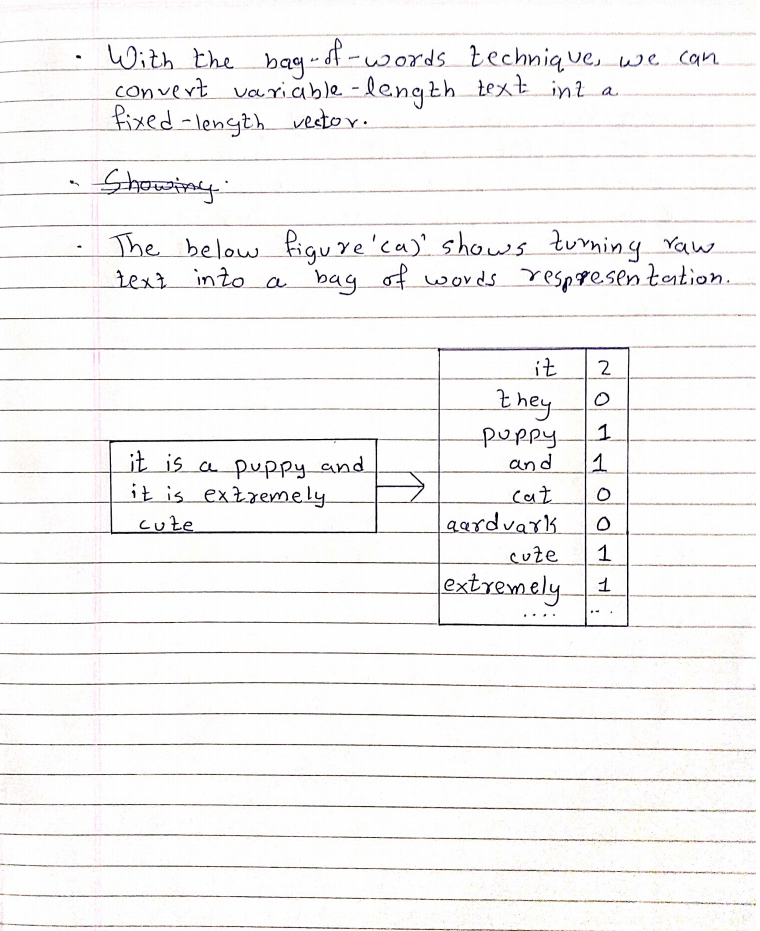
Q2. Explain a bag of words model in detail.
Ans:

Q3. Why python? List the libraries you can used in python.
Ans:


Q4. Discuss the role of indentation in python.
Ans:


Q5. (i) Write a python program to find the factorial of a given number using
recursion.
(ii)Write a python program to print the Fibonacci sequence.
Ans: 

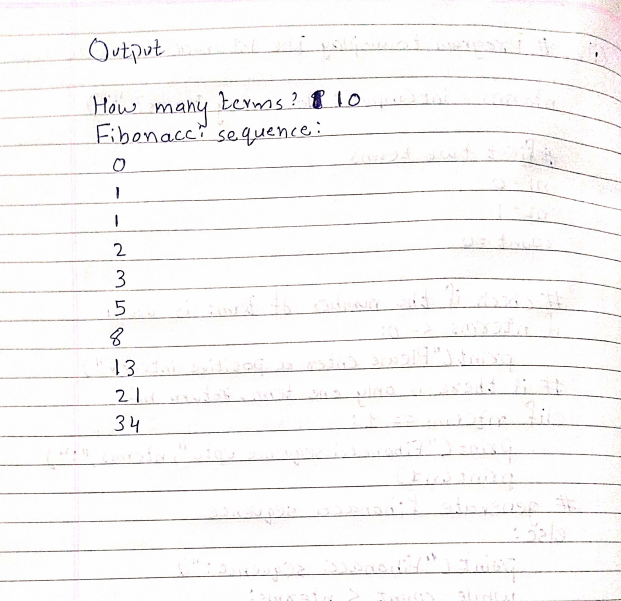

Q6. Explain identity and membership operator with example.
Ans:




Q7. Explain range() function with suitable examples.
Ans:
Python range() function:
-
range() is a built-in function of Python. It is used when a user needs to perform an action for a specific number of times. range() in Python(3.x) is just a renamed version of a function called xrange in Python(2.x). The range() function is used to generate a sequence of numbers.
-
range() is commonly used in for looping hence, knowledge of the same is the key aspect when dealing with any kind of Python code. The most common use of the range() function is to iterate sequence type (List, string, etc.. ) with for and while loop.
-
In simple terms, range() allows the user to generate a series of numbers within a given range. Depending on how many arguments the user is passing to the function, the user can decide where that series of numbers will begin and end as well as how big the difference will be between one number and the next. range() takes mainly three arguments.
Following are the range function parameters that we use in python:
- start: This is the starting parameter, it specifies the start of the sequence of numbers in a range function.
- stop: It is the ending point of the sequence, the number will stop as soon as it reaches the stop parameter.
- step: The steps or the number of increments before each number in the sequence is decided by the step parameter.
Syntax: range(start, stop, step)
Example 1:
# range() with one parameter
for n in range(5):
print(n, end = " ")
print()
# range() with two parameter
for n in range(5, 10):
print(n, end = " ")
print()
# range() with three parameter
for n in range(1, 10, 2):
print(n, end = " ")
Output:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 3 5 7 9Example 2:
#Python Program to show range() basics
# printing number
for i in range(10):
print(i, end =" ")
print()
# using range for iteration
l = [10, 20, 30, 40]
for i in range(len(l)):
print(l[i], end =" ")
print()
# performing sum of natural number
sum = 0
for i in range(1, 11):
sum = sum + i
print("Sum of first 10 natural number :", sum)
Output:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 20 30 40 Sum of first 10 natural number : 55

Q8. Write a python program to read data from CSV files using pandas.
Ans:

Q9. Write a python program to read data from a text file using pandas library.
Ans:

Q10. List the type of plots that can be drawn using matplotlib.
Ans: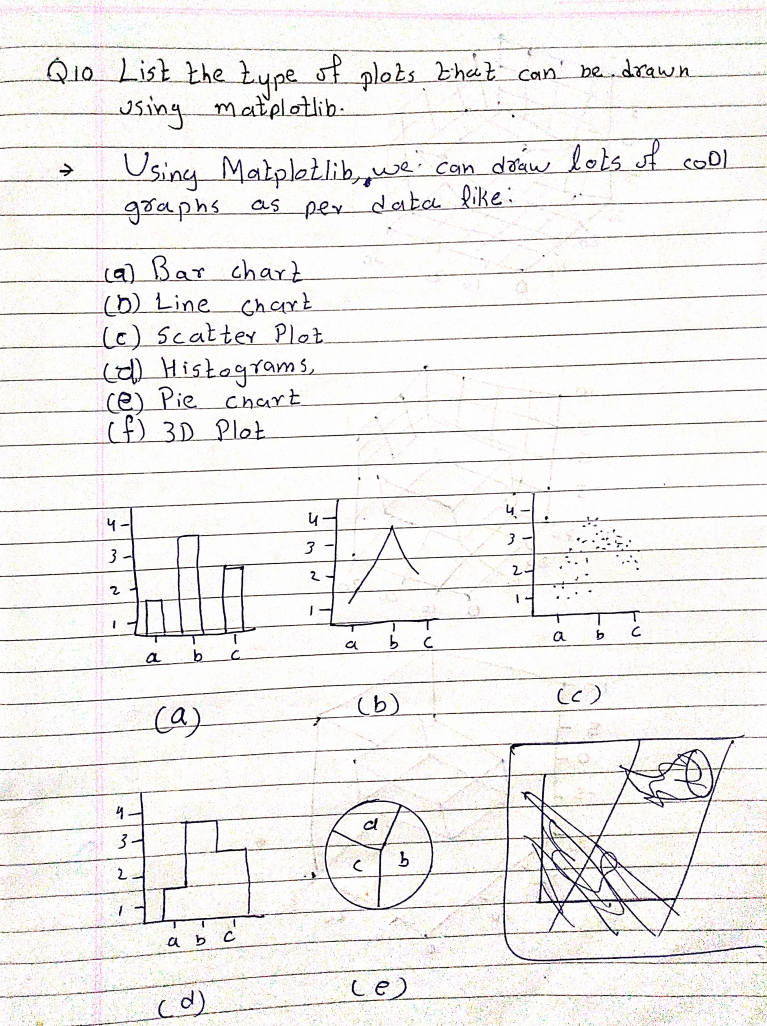

Q11. Describe date time transformation using datetime module.
Ans:






Q12. Explain TF-IDF transformations.
Ans:
Q13. Explain categorical variables in detail.
Ans:
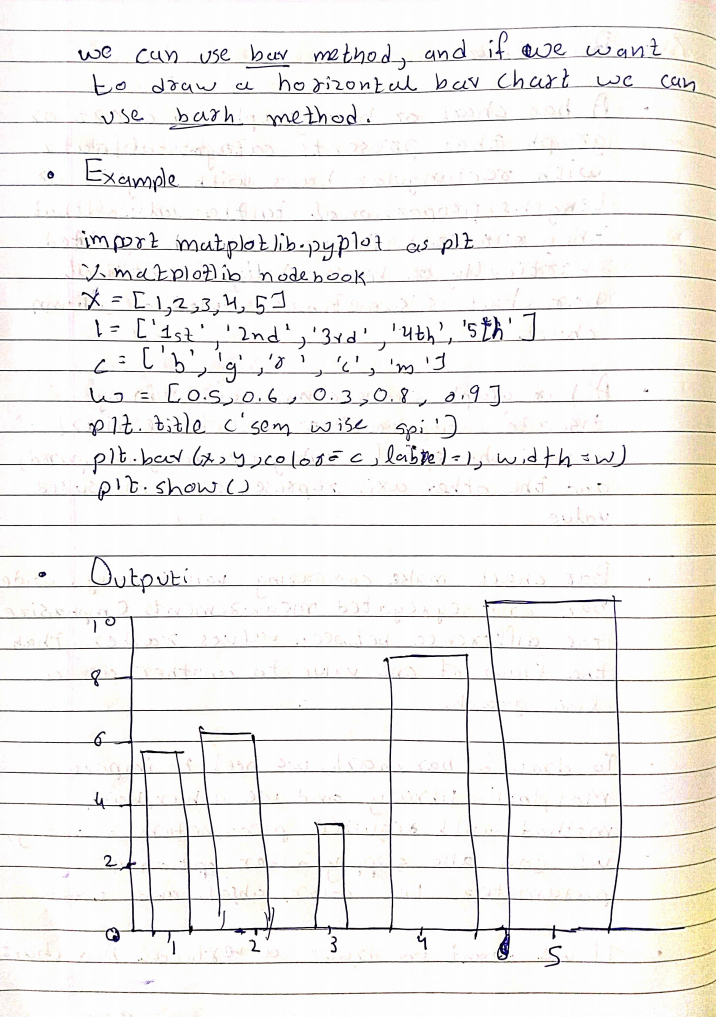
Q14. Explain pie chart and bar chart plot with appropriate examples.
Ans: